Nano-robots, that may walk through veines and cure diseases like cancer and hepatitis C by killing the affecting cells in patient’s body and may practice in other future invensions. Some researchers developed nano-robots that can target different diseases. It’s just a one application of nano-robots but, they will have broader applications in near future.
‘Nano’ is derived from the greek word ‘nannos’, which means ‘dwarf’. Nano-robots are creating from Nano particles which are 10-9 part of a meter. They are not bigger than thousandth of millimetre and can be even smaller. They are ranging in size from 0.1 to 10 micrometers. Other names of Nano-robots are nanobots, nanoids, nanites, nanomachines or nanomites. Nanorobots are currently in research and development but, some researchers have tested nano-robots on diseases like hepatitis C.
What will be the mode of working
Nano-robots have major applications in medical field. Researchers are working on nano-robots around the world to design these tiny machines to implement in various industries. nano-robots can be implemented in unlimited ways by programming them according to the specific application. nano-robots actually plays a role of transportation of payloads to the targeted area. In this way medicines work effectively and have quick results in patients. In other way if, same medicine is given in traditional way, it goes through immune system then in bloodstream and lastly reaches at infected area. In this whole process only a small quantity of antibiotic is delivered at the infected area and it also take more time through immune system.
Research that is being carried out on magnetic nano-robots suggests that they can be released in blood and can attach themselves to cancerous growths. If the rotating magnetic field is applied to the body of the cancer patient, the small magnetic robots in the cancerous tissue would start rotating. As a result, the cancerous growth would heat up and die.
It’s also effective in patients with liver diseases whose immune systems can not process antibiotics, and medicines are unable to directly impact on infected areas.
Developed Nano-robots
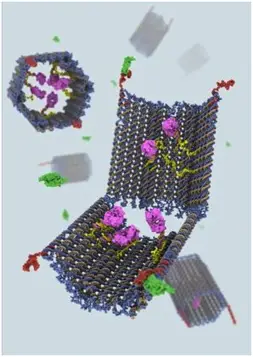 Harvard University & University of Florida developed cancer and Hepatitis C killing nano-robots. UF researchers develop nano-robots that can be programmed to target different diseases. They have successfully tested these nano-robots on hepatitis C patients. They believe that programmable nature of these particles makes it potentially useful against diseases such as cancer and other viral infections. These tiny machines can target any specified cell by programming them accordingly and leave healthy cells unharmed.
Harvard University & University of Florida developed cancer and Hepatitis C killing nano-robots. UF researchers develop nano-robots that can be programmed to target different diseases. They have successfully tested these nano-robots on hepatitis C patients. They believe that programmable nature of these particles makes it potentially useful against diseases such as cancer and other viral infections. These tiny machines can target any specified cell by programming them accordingly and leave healthy cells unharmed.
For demonstration, researchers Cao and colleagues created and tested a particle that targets hepatitis C virus in the liver and prevent the virus from making copies of itself. More than 3 million people in the United States are infected and about 17,000 new cases are diagnosed each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current hepatitis C therapies are partially effective and leave side effects from one medication to another.
According to researchers in laboratory tests, the treatment led to almost a 100 percent decrease in hepatitis C virus levels. In addition, it did not trigger the body’s defense mechanism, and that reduced the chance of side effects. Still, additional testing is needed to determine the safety of the approach.
Researchers at Harvard developed complex thee dimensional structures and objects by using DNA origami method. A team of researchers created a nanosized robots in the form of an open barrel at Bar-llan University in Israel. DNA barrel which act as a container is held by special DNA latch that can recognize and seek out combinations of cell surface proteins, including disease markers. When the latches find their targets, they reconfigure, causing the barrel to swing open and expose its contents or payload. Container barrel can hold various types of payloads, including specific molecules with encoded instructions that can interact with specific cell surface signalling receptors.
“We can finally integrate sensing and logical computing functions via complex, yet predictable, nanostructures — some of the first hybrids of structural DNA, antibodies, aptamers and metal atomic clusters — aimed at useful, very specific targeting of human cancers and T-cells,” said George Church, Ph.D., a Wyss core faculty member and Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School, who is Principal Investigator on the project.
But there are some complications, because DNA is a natural biocompatible and biodegradable material, DNA nanotechnology is widely recognized for its potential as a delivery mechanism for drugs and molecular signals and significant challenges to its implementation, such as what type of structure to create; how to open, close, and reopen that structure to insert, transport and deliver a payload and how to program this type of nano-scale robot.
We would expect nano-robots fighting cancer & other diseases in the near future.
Image: Harvard


Comments