- iPhone 16 battery will be easier to replace, thanks to EU
- Apple Intelligence will also come to the Vision Pro, the HomePod will not have the same luck

Following Apple’s announcement that it will not launch its artificial intelligence ecosystem, Apple Intelligence, in the European Union (EU), the European Commission expressed concern. Margrethe Vestager, executive vice president of the organization, said that it was anti-competitive behavior on the part of the company.
“They say they will not do it because of the obligation they have in Europe and the obligation they have in Europe is to be open to competition. This is the abridged version of the Digital Markets Act (DMA),” Vestager said at Forum Europa. “I find it very interesting that they say that they will now deploy AI where they are not obliged to allow competition,” he added.
“I think it’s the most open and surprising statement that they know 100% that this is another way to disable competition,” said the Danish politician.

What the EU’s claims about Apple mean
Mentioning that Apple plans to deploy its AI in regions where the obligations required by the DMA do not apply, Vestager expressed concern about what she sees as a strategy to avoid fair competition.
What the DMA requires of tech companies
The DMA (Digital Markets Act) requires several points for technology companies that are designated as gatekeepers or gatekeepers in the digital market. Here are some of the main requirements:
– Interoperability: Companies must ensure that their services are interoperable with other services and systems, allowing users to easily switch between different platforms and applications.

– Prohibition of anti-competitive practices: It is forbidden to carry out practices that distort competition, such as self-preference, unfair discrimination or the imposition of unfair contractual conditions on users.
– Data access: They must provide access to key data to competitors and users, under certain conditions, to foster innovation and competition in the market.
– Transparency: Companies must be transparent in their business practices, including publishing reports on their performance, terms and conditions, and data processing policies.
– Prohibition of restrictive clauses: The inclusion of clauses in contracts that limit the ability of users to use third-party or alternative services is not allowed.
– Notification and consultation: Companies must notify the European Commission of any significant acquisitions or changes to their services that may affect competition in the digital market.
What does it mean for a company to be anti-competitive?
Being anticompetitive involves any action that has the effect of restricting genuine and fair competition in the market, benefiting the company to the detriment of consumers and other market participants.
Why Apple is considered an access gatekeeper
Apple is considered an “access gatekeeper” under the DMA (Digital Markets Act) due to its dominant position in the digital market. This designation is based on several key factors including:
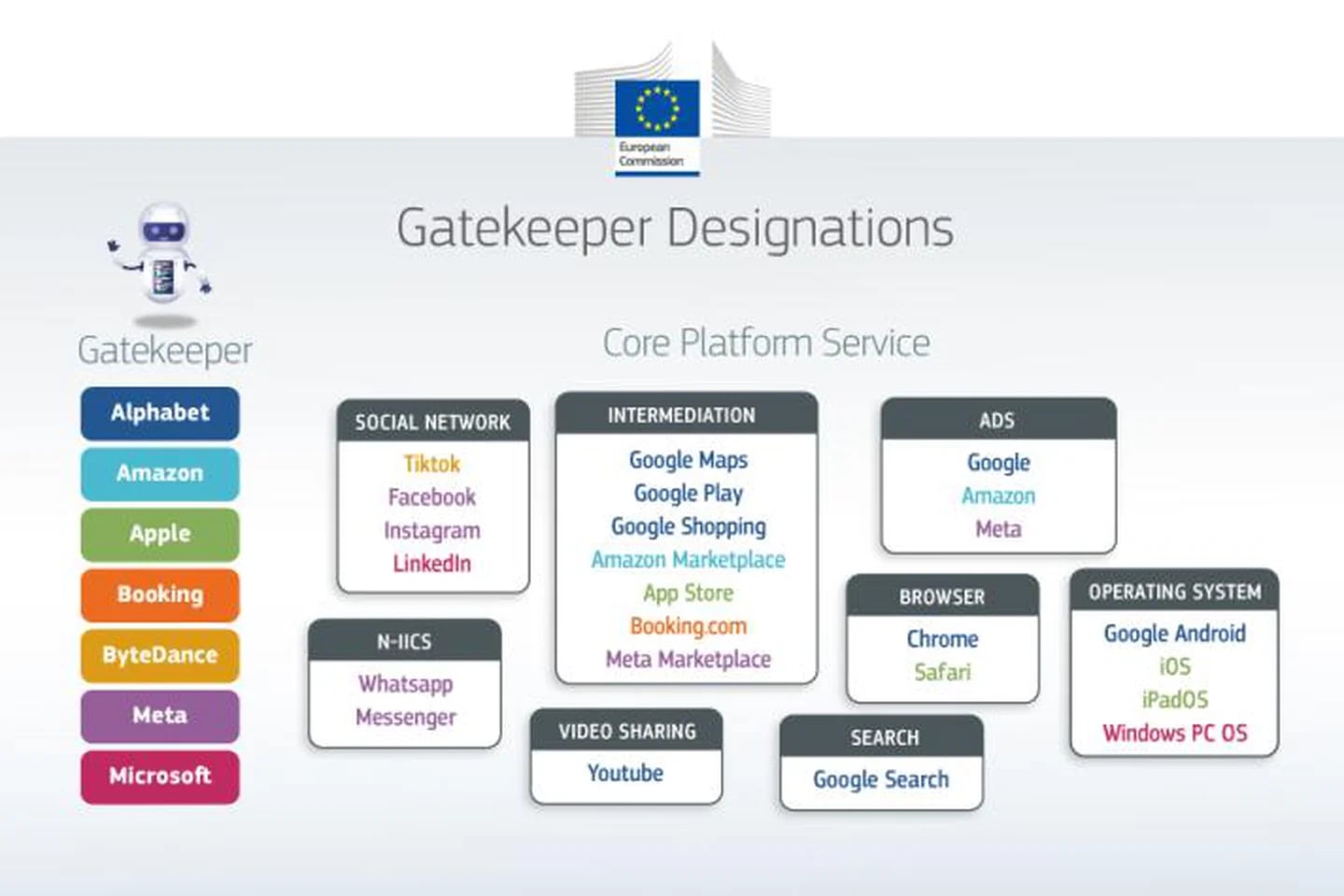
– Strong economic position: The firm led by Tim Cook has a strong economic position, with a turnover of more than 7,500 million euros in annual turnover, a market capitalization of more than 75,000 million euros and at least 45 million monthly active users in the EU.
– Control over digital platforms: Apple manages closed ecosystems such as iOS and iPad OS, where it controls the distribution of applications through the App Store and sets rules and conditions for developers and users.
– User base and broad market: With millions of active users in the European Union and a wide range of services built into its devices, Apple has considerable influence over how digital services are developed and operated in its ecosystem.

Comments